Virus in Biology
A virus is an extremely small infectious particle that is not truly living but can reproduce inside a host cell. It contains genetic material (DNA or RNA) wrapped in a protein coat. The study of viruses is called virology.
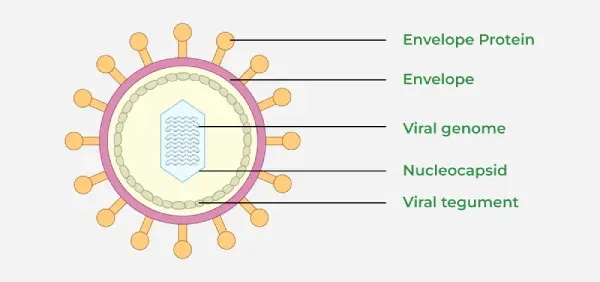
Characteristics of Virus
The following are a few of its characteristics :
- Viruses are submicroscopic organisms. They are even smaller than bacteria.
- They are non-cellular and lack cell organelles.
- Viruses are obligate parasites that act as connecting links between the living and the non-living organisms.
- Viruses contain protein and genetic material that can be either DNA or RNA, but can never be both.
- Their genetic material is protected by a protein covering called the capsid.
- The capsid is made up of small subunits called Capsomeres.
- Some viruses have an external lipid membrane called an Envelope.
Classification of Virus
1. Classification of viruses based on the type of nucleic acid
| DNA virus | RNA virus |
|---|---|
| DNA genetic material | RNA genetic material |
| Single-stranded(ss): Parvovirus | Double-stranded(ds): Reovirus |
| Double-stranded(ds): Herpesvirus | Single-stranded(ss): Poliovirus, Rabies |
2. Classification of Viruses Based on Host
| Plant Viruses | Animal Viruses | Bacterial Viruses |
|---|---|---|
| Infects plants | Infects animals | Infects bacteria |
| Mostly RNA | DNA and RNA | Mostly DNA |
| Example: TMV | Example: HIV, Influenza | Example: T4 bacteriophage |
3. Classification of Viruses Based on Structure
| Type of Virus | Example |
|---|---|
| Cubical virus | Picorna virus, Reovirus |
| Radial symmetry virus | Bacteriophage |
| Spiral virus | Orthomyxovirus |
| Complex virus | Pox virus |
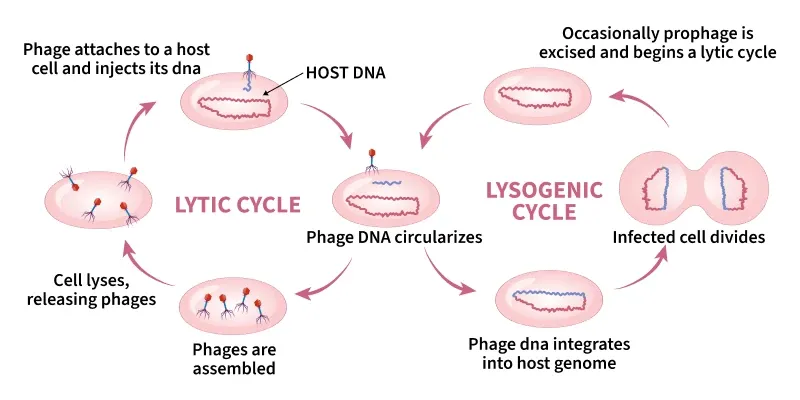
Reproduction in a Virus
Steps: Attachment, Penetration, Uncoating, Replication, Assembly, Release. Cycles: Lytic Cycle (fast, destructive) and Lysogenic cycle (dormant phase).
Diseases caused by a Virus
| Diseases | Description |
|---|---|
| AIDS | Caused by HIV, infects immune system |
| Chickenpox | Varicella-zoster virus |
| Measles | Measles virus |
| Mumps | Mumps virus |
| Herpes | Herpes Simplex Virus |
Importance of Virus
- Vaccine production
- Evolutionary links
- Molecular biology studies
- Drug delivery vectors
- Pest management