Symbiosis and Symbiotic Relationship
Symbiosis is a close, ongoing relationship between two different species in an ecosystem.

Types of Symbiosis
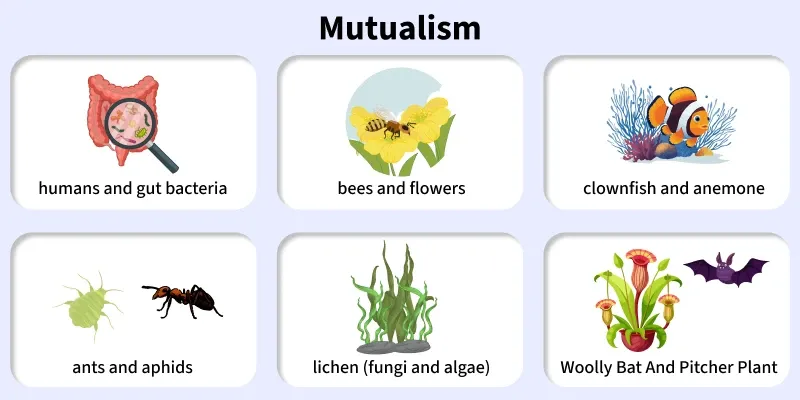
Mutualism
Both species benefit. Example: Bees and flowers.
- Obligate Mutualism: Necessary for survival (e.g., mycorrhizal fungi).
- Facultative Mutualism: Beneficial but not essential (e.g., oxpeckers).
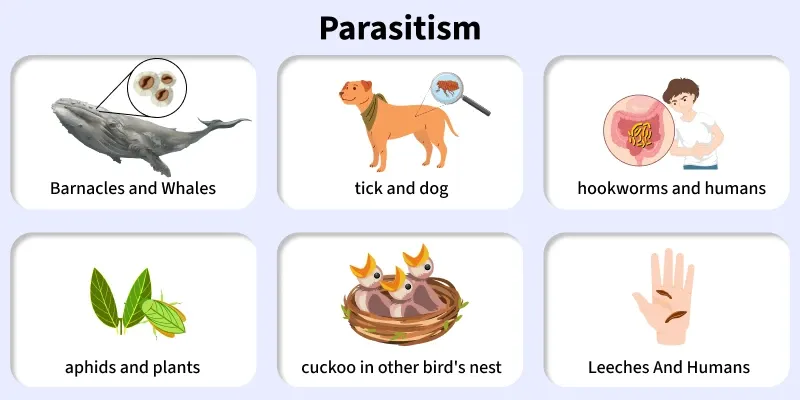
Parasitism
One benefits at the expense of another. Example: Ticks, tapeworms.
- Endoparasitism: Inside host.
- Ectoparasitism: Outside host.
Commensalism
One gains, other is unaffected. Example: Barnacles on whales.

- Phoresy: Transportation.
- Epiphytism: Support (e.g., orchids on trees).
Advantages of Symbiosis
- Resource conservation
- Nutrient Exchange
- Reproductive benefits
- Increased Biodiversity