Cell Division
Cell division is the process where a parent cell splits to form daughter cells, essential for growth and reproduction.
Types of Cell Division
- Mitosis (Equational Division): Results in two genetically identical daughter cells (2n -> 2n). Used for growth and tissue repair.
- Meiosis (Reductional Division): Results in four unique haploid daughter cells (2n -> n). Used for gamete production (sperm/egg).
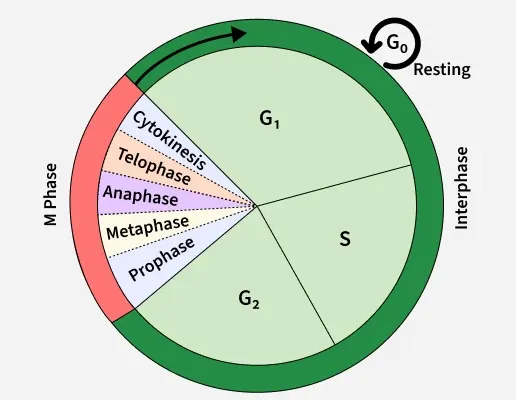
The Cell Cycle
- Interphase: G1 (Growth), S (DNA replication), G2 (Preparation for division).
- M Phase: Mitosis (Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase) and Cytokinesis.
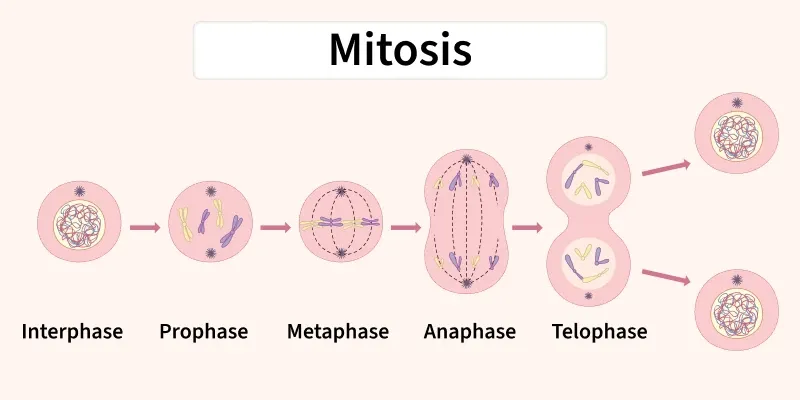
Stages of Mitosis
- Prophase: Chromosomes condense.
- Metaphase: Chromosomes align at the equator.
- Anaphase: Sister chromatids separate.
- Telophase: Nuclear envelopes reform.